How to Say “Yes” and “No” in Morse Code

The importance of simple yet powerful affirmations and negations cannot be overstated in human interaction.
"Yes" and "No" are the unsung communication heroes, the backbone of agreement and disagreement. These two words traverse language barriers, cultural divides, and social intricacies, serving as the bedrock of understanding.
In this guide, we will learn different ways to say "Yes" and "No" using Morse code. It is like a secret code language, and by the end of it, you will be able to use it, too.
So, let's dive into this cool Morse code stuff and discover new ways to show agreement or disagreement. Get ready for some language fun!
The Morse Code Alphabet
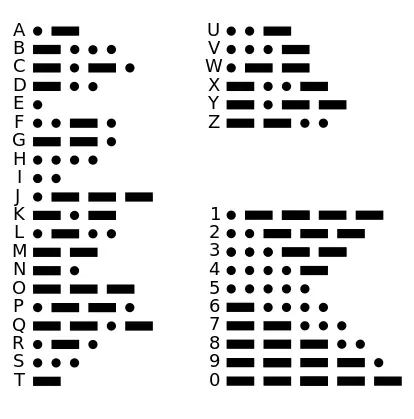
Before delving into the representation of "Yes" and "No" in Morse Code, we must familiarize ourselves with the Morse Code alphabet.
Each letter and numeral has its distinct pattern of dots and dashes.
For example, the letter "A" is represented by a dot followed by a dash (.-), while the letter "B" is represented by a dash followed by three dots (-...).
This binary system of short and long signals allows for transmitting messages through audible or visual cues.
Ready for more Morse Code magic? Try Morse Code Translator to uncover the secrets of other alphabets and beyond.
How to Say “Yes” in Morse Code
The affirmative response, "Yes," is expressed in Morse Code using the combination of three letters: "Y", "E," and “S.”
Let's break down the Morse Code representation of each letter and then combine them to form the representation of "Yes."
Y in Morse Code:
The letter Y is represented by a dash followed by a dot and then two more dashes (-.--).
E in Morse Code:
The Letter E is represented by a single dot (.).
S in Morse Code:
The Letter S is represented by three dots (...).
Now, combining the Morse Code representations of Y, E, and S, we get:
Morse Code for Yes: -.-- . ...
This sequence of dots and dashes, when transmitted through sound, light, or touch, conveys the affirmative response "Yes" in a manner that can be universally understood by Morse Code users.
How to Say No in Morse Code
On the contrary, the negative response, "No," is conveyed through the Morse Code representations of the letters "N" and "O." Let's examine the Morse Code writing patterns for these letters and then combine them to form the representation of "No."
N in Morse Code:
The Letter N is represented by a dash followed by a dot (-.).
O in Morse Code:
The Letter O is represented by three dashes (---).
Now, combining the Morse Code representations of N and O, we get:
Morse Code for No: -. ---
Similar to the representation of "Yes," the sequence of dots and dashes for "No" can be transmitted through various mediums, allowing the negative response to be communicated in Morse Code.
How to Speak “Yes” and “No” in Morse Code
Speaking "Yes" and "No" in Morse Code involves translating the dots and dashes into audible signals “di” and “dah”. Here is how you can articulate Yes and No in Morse Code:
Speaking "Yes" in Morse Code:
To vocalize Yes in Morse Code, you can use the following pattern:
"Yes" in Morse Code: "dash dot dash dash dot dot dot dot" (-.-- . ...)
When spoken, this translates to "dah-di-dah-dah dit di-di-dit"
Speaking "No" in Morse Code:
To convey No in Morse Code through speech, you can use the following sequence:
"No" in Morse Code: "dash dot dash dash dash “(-. ---)
When spoken, this translates to "di-dah dah-dah-dah"
Remember, the key is to maintain a clear distinction between the dots and dashes, creating a rhythmic and easily distinguishable pattern for the listener. Whether using sound, light, or touch, Morse Code's simplicity and versatility make it a fascinating mode of communication that transcends traditional language barriers.
“Yes” and “No” in Morse Code With a Flashlight
Expressing "Yes" and "No" in Morse Code using a flashlight is a practical and engaging way to communicate when spoken language is ineffective. Morse Code utilizes a series of short and long signals translated into light signals in this context.
Follow the Morse code spacing rules with light to the context of conveying "Yes" or "No":
- The time gap between dots and dashes is 1 second with the light off:
When sending Morse Code for "Yes" or "No" using light signals, each dot or dash is represented by turning the light on for a specific duration, let's say 1 second. The absence of light during this 1-second interval signifies the space between dots and dashes.
- The time gap between full letters is 3 seconds with the light off:
For clarity in communication, the space between complete letters is maintained by turning off the light for 3 seconds. This break helps distinguish individual letters in the Morse Code message.
- The pause between complete words is 7 seconds with the light off:
To indicate the end of a word, a longer pause of 7 seconds with the light off is introduced. This extended break serves as the separation between distinct words in the Morse Code message.
The distinctiveness of the patterns ensures that messages are easily understood, making Morse Code with a flashlight a valuable skill in various contexts.
Blinking “Yes” or “No” in Morse Code
Blinking "Yes" or "No" in Morse Code involves using a series of intentional blinks to represent the dots and dashes of Morse Code.
Ensure the blinks are deliberate and distinguishable, with longer blinks (Close eyes for 3 seconds) serving as dashes and shorter (Close eyes for 1 second) as dots. This method can be a fun and practical way to communicate in situations where verbal communication may not be feasible, making Morse Code a versatile and entertaining skill.
Procedure for sending "Yes" or "No" in Morse Code with eye blinks:
Step 1: Establish Eye Contact:
Ensure you have the attention of your communication partner.
Establish a clear line of sight for effective eye communication.
Step 2: Understand Morse Code:
Familiarize yourself and your partner with Morse Code for "Yes" (-.-- . ...) and "No" (-. ---).
Step 3: Blink According to Morse Code:
For "Yes":
Y: dash, dot, dash, dash
E: dot
S: dot, dot, dot
Blink according to the Morse Code pattern for "Yes." For example, one blink for each dot and two blinks for each dash in "dash dot dash dash dot dot dot dot" (- . - - . . . .)
Maintain a consistent and clear pattern for an easy interpretation.
For "No"
N: dash, dot
O: dash, dash, dash
Blink according to the Morse Code pattern for "No." For example, two blinks for each dash and one blink for each dot in “dash dot dash dash dash" (- . - - -)
Keep the pattern distinct from "Yes" to avoid confusion.
Step 4: Allow Your Partner to Respond:
After conveying your message through eye blinks, give your partner a moment to process and respond.
Encourage them to blink their response using the same Morse Code system.
Step 5: Enjoy the Moment:
Interpret the responses based on the agreed-upon Morse Code system.
Use this non-verbal communication method to enjoy a unique and interactive experience with your partner.
Some Important Tips:
- Practice beforehand to ensure clear and consistent eye blinks.
- Agree on a suitable duration for blinks and pauses.
- Maintain a relaxed and comfortable environment for effective communication.
- Be patient and attentive during the communication process.
- Remember that this method relies on mutual understanding and practice between communication partners. Adjust the procedure according to personal preferences and comfort levels.
How Do You Tap “Yes” or “No” In Morse Code?
If you want to say “Yes” or “No” through tapping covertly, here's a unique way:
Tap Your Message:
Tap your message to discreetly convey your message.
Close Proximity Tapping:
When near each other, tap on a table or wall to share each letter of your message without drawing attention.
Tools for Tapping:
Utilize your fingers, a pen, or any item that can produce audible taps, ensuring your communication remains inconspicuous.
Timing Rules for Dots and Dashes:
- Abide by specific timing rules for dots and dashes in Morse Code tapping.
- For dots, execute a brief tap and follow it with a 1-second pause.
- For dashes, tap with a longer duration and pause for 3 seconds.
Example – Tapping the Letter Y:
If tapping out the letter Y(- . - -), tap once and pause for 3 seconds, then tap and wait for one second, and then 2 taps with the pauses of 3 seconds for dashes after each tap.
Post-Letter Pause:
After completing the tapping for Y, take a break for 3 seconds to signify the end of that letter.
End-of-Word Pause:
Upon finishing the entire word, indulge in a pause of 7 seconds to signal the conclusion of your message.
By following these rules, your covert tapping can effectively convey Morse Code messages without attracting undue attention. Adjust the tapping duration based on your comfort and your communication setting.
Morse Code for “YES” or “NO” in other Languages
Let's delve into how Morse Code represents affirmatives and negatives in some major languages:
Expressing "Yes" in Morse Code:
- In Spanish (si): ... ..
- In French (oui): --- ..- ..
- In German (ja): .--- .-
Expressing "No" in Morse Code:
In Spanish ("no"): -. ---
In French ("non"): -. --- -.
In German ("nein"): -. . .. -.
Using Morse Code, we establish a common ground between languages, offering a universal means to convey basic affirmations and negations. This system enables effective non-verbal communication, fostering understanding and connection among people of different linguistic backgrounds.
Also, explore our article on how to express I Love You in Morse code.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the Morse Code is a fascinating and valuable means of communication. Its concise representation of "Yes" and "No" through dots and dashes provides a universal language for affirmations and negations. Whether spoken, flashed with a flashlight, or blinked intentionally, Morse Code transcends linguistic barriers, offering a versatile and entertaining skill. Its practicality shines in emergencies or outdoor activities, reinforcing its relevance even in our technologically advanced era. Morse Code is a timeless bridge, connecting people across languages through fundamental expressions of agreement and disagreement.