How to Write in Morse Code: 5 Easy Steps

Morse Code is a method of encoding text characters into sequences of two different signal durations. These signals are typically referred to as dots and dashes or, more formally, short and long signals.
It was created by Samuel Morse and Alfred Vail in the early 1830s, and it's still used today. It has played crucial roles in both military and civilian contexts throughout history.
Despite the expansion of modern communication technologies, Morse code remains an interesting skill for amateur radio operators and enthusiasts.
In this blog, we will discuss the basics of how to write in Morse code using five simple steps.
How to Write Morse Code in 5 Steps
Starting to write in Morse code is simple, thanks to its universal alphabet mapping and unique communication method. Using a Morse Code Translator is handy as it simplifies the process.
Step 1: Find the Morse Code Translation for Your Message
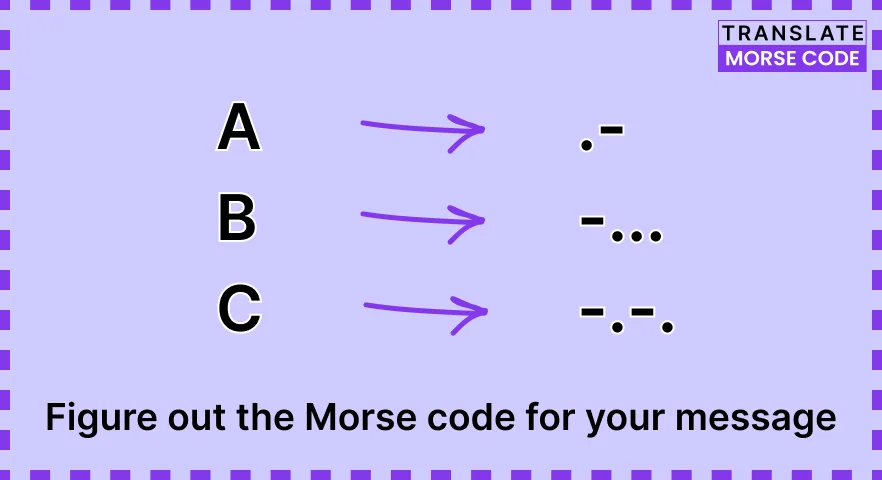
The first step in Morse code writing is to find the Morse code translation for the message you intend to convey.
When it comes to writing in Morse code, there are two primary approaches you can choose from. Both methods are effective, and your preference may depend on your style and convenience.
Method 1: Writing Morse Code Directly
One straightforward way to write in Morse code is to represent each letter and word by the dot and dash signals themselves.
For example, if you want to write the word "hello" in Morse code, it would look like this: ".... . .-.. .-.. ---".
You may use a dash (-) or an underscore (_) to represent the space between each signal; we will use the dash in our examples for consistency.
This method is faster and simpler, especially once you have familiarized yourself with the Morse code representations for each character. You directly write out the sequence of dots and dashes for each letter and word, making it easy to transmit or interpret the message.
Method 2: Using "Dit" and "Dah"
Alternatively, you can opt for a more phonetic approach to writing in Morse code.
In this method, you spell out the dot and dash signals based on how they sound. You will use the terms "dit" for dots and "dah" for dashes to represent Morse code signals.
For instance, if you are spelling "hello," you would write it as "dit-dit-dit-dit-dit-dit-dah-dit-dit-dit-dah-dit-dit dah-dah-dah."
This approach can be especially helpful for beginners who are just getting acquainted with Morse code, as it helps you understand the rhythm and sound of the code.
By vocalizing "dit" and "dah," you can create a mental connection between the sound and the corresponding Morse code signal.
Over time, this can aid in writing and deciphering Morse code messages.
Step 2: Put a Space After Each Letter
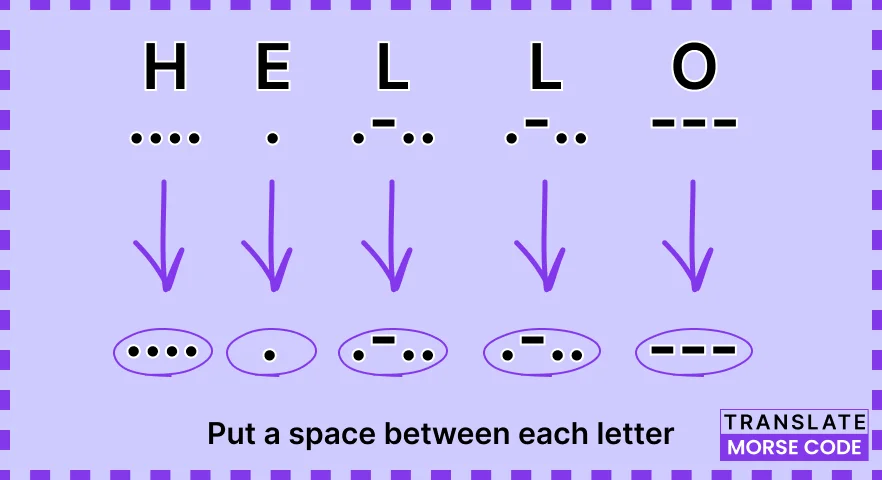
To ensure that the Morse code for each character is accurately interpreted, it is crucial to insert a space after each letter.
This space helps prevent the individual characters from blending together, ensuring they remain distinguishable.
Step 3: Write a Slash After Each Word
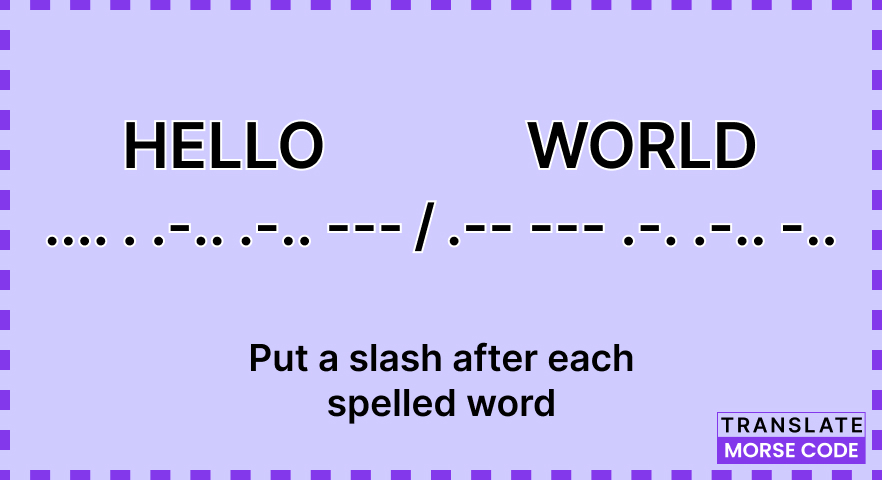
In Morse code, words are separated by a slash (/). After you have completed representing a word, insert a slash to indicate the end of that word and the beginning of the next. Without these word separators, the Morse code message would be a continuous stream of dots and dashes, making it extremely challenging for the recipient to decipher.
Let us look at an example to illustrate the importance of writing a slash after each word:
Example: "HELLO WORLD" in Morse Code
When writing the phrase "HELLO WORLD" in Morse code, you would first translate each letter into its respective Morse code representation. Here is the Morse code for each letter:
H: "...."
E: "."
L: ".-.."
L: ".-.."
O: "---"
W: ".--"
O: "---"
R: ".-."
L: ".-.."
D: "-.."
Now, when you write this message in Morse code, you will use spaces to separate individual letters and slashes to separate words. Here is how it looks:
.... . .-.. .-.. --- / .-- --- .-. .-.. -..
In this example, you can see that there is a space between each letter and a slash between the words "HELLO" and "WORLD." This clear word separation makes it much easier for the recipient to interpret the message accurately.
Step 4: Treat Punctuation as a Letter in the Word
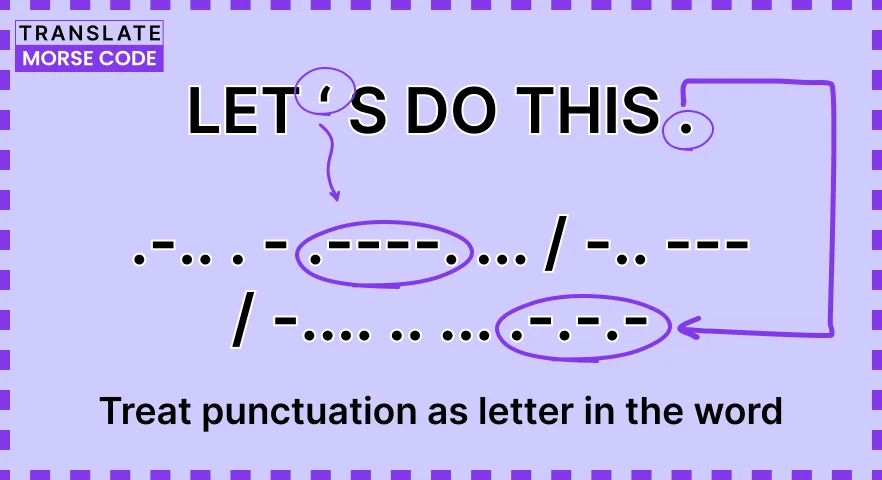
In Morse code, punctuation marks are treated as if they were letters within a word. This means that each punctuation mark is assigned a specific Morse code representation, and it is included as part of the Morse code for a word, similar to how letters are encoded.
This practice ensures that the recipient can accurately decode the entire message, including punctuation.
Example: "HELLO, WORLD!" in Morse Code
Suppose you want to write the phrase "HELLO, WORLD!" in Morse code. In this case, you will assign Morse code representations to the punctuation marks, such as the comma and exclamation marks.
Here are the Morse code representations for these punctuation marks:
Comma (,): "--..--"
Exclamation Mark (!): "-.-.--"
Now, when you write the message in Morse code, you will include these punctuation marks within the word, just like any other letter. Here is how it looks:
.... . .-.. .-.. --- --..-- / .-- --- .-. .-.. -.. -.-.--
In this example, you can see that the comma (,) and exclamation mark (!) are included within the Morse code for "HELLO, WORLD." This practice ensures that the message is transmitted accurately and that the recipient can interpret not only the words but also the intended punctuation.
Step 5: Don’t Use Capitalization in Morse Code
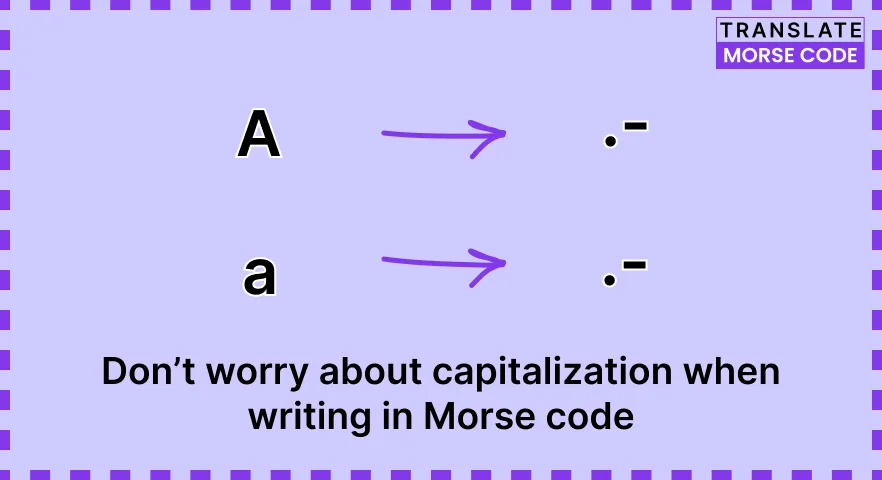
Morse code does not differentiate between uppercase and lowercase letters. Hence, you need not concern yourself with capitalization when writing in Morse code. Stick to the standard Morse code representations for all letters, irrespective of their case.
How to Write Sentences in Morse Code
Now that you have acquired the fundamental steps for writing in Morse code, you can begin crafting complete sentences and messages.
Start by translating each letter into Morse code using either the visual chart or audio signals. Remember to insert spaces between letters and slashes between words.
If your message includes punctuation, ensure you include the appropriate Morse code representations for these symbols.
When transmitting your message, you can use various means of communication, such as flashing a light, sounding a buzzer, or tapping out the signals. It is essential to maintain a consistent rhythm and timing for each dot and dash to ensure the accurate transmission and reception of your message.
Here are some examples of English sentences translated into Morse code, along with their Morse code representations:
- Example 1: "YOU ARE CUTE"
- Morse Code: “-.-- --- ..- / .- .-. . / -.-. ..- - ."
- Example 2: "GOOD MORNING"
-
- Morse Code: "--. --- --- -.. / -- --- .-. -. .. -. --."
- Example 3: "I LOVE YOU"
-
- Morse Code: ".. / .-.. --- ...- . / -.-- --- ..-"
- Example 4: "THANK YOU"
-
- Morse Code: "- .... .- -. -.- / -.-- --- ..-"
- Example 5: "GOODBYE, FRIENDS"
-
- Morse Code: "--. --- --- -.. -... -.-- . / ..-. .-. .. . -. -.. ... / --. --- --- -.. -... -.-- ."
- Example 6: "MORSE CODE IS FUN"
-
- Morse Code: "-- --- .-. ... .-.-. -.-. --- -.. . / .. ... / .. ... / ..-. ..- -."
These examples demonstrate how to write a sentence in Morse code by translating English words and phrases into their respective Morse code representations.
Related Read: How to say yes and no in Morse code
Conclusion
In conclusion, writing in Morse code may appear daunting at first, but with practice and a solid understanding of the fundamentals, it becomes a fascinating and useful skill. Morse Code's simplicity, versatility, and historical significance have allowed it to remain a valuable tool for communication enthusiasts worldwide. Following the five easy steps outlined in this comprehensive guide, you can confidently embark on your journey to write and transmit messages in Morse code.